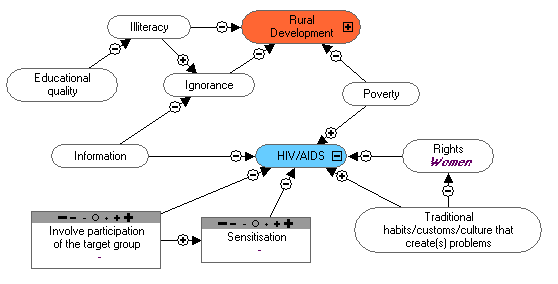
 |  | Africa's Sustainable Development Council |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Salibo
Somé
ASUDEC is a non-confessional,
non-governmental, apolitical, and
non-profit organisation.
Objectives:
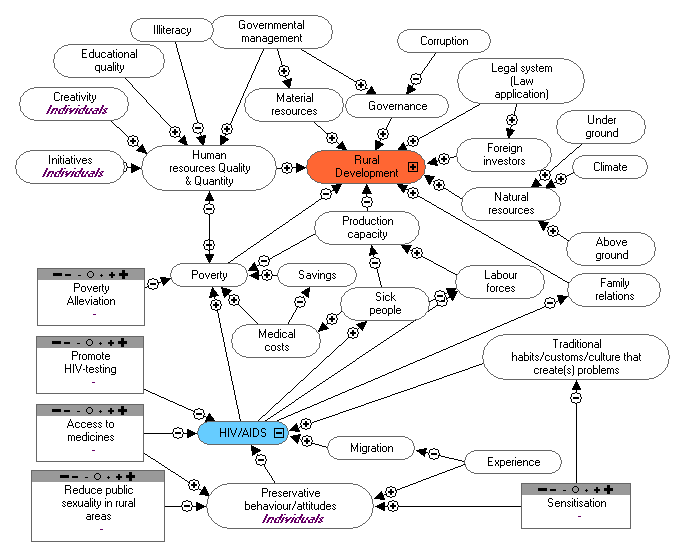
1. Poverty alleviation.
2. Improvement of children's educational
level.
3. Reduction of illiteracy and ignorance of the
population.
4. Environmental protection.
|
 |  | Association for Peace and Solidarity |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Keivin H. Ouedraogo
Objective:
Poverty alleviation, for all target groups (women,
peasants and youth in the rural areas)
|
 |  | Association of Environmental Protection and Restoration |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Yacouba Traore
Objectives:
1. Being responsible and try to achief an
effective participation of the populations to fight
against the desertification and favour
agricultural, sylvicultural and pastoral activities
for environmental reconstruction.
2. To make the population conscience and
self-reliant towards the aspects of primary
health.
3. To promote women activities and to lighten
women's daily activities, especialy rural women.
|
 |  | Bougouriba Provincial Livestock Authorities |
| |
Diebougou, Mr. Kabre Ambroise
Objectives:
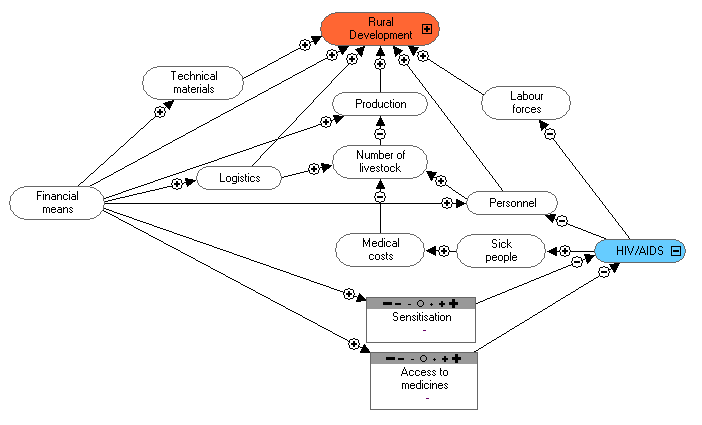
1. To control the production of livestock, with regard to cattle, sheep, goats and chickens.
2. (In Burkina Faso there is a lack of financial means).
We train the producers (livestock) so that they can increase their yields:
- Increase livestock breeding
- Zero grazing, for quick production and returns
3. Our main objective is still alleviating poverty.
In Burkina Faso, 90% of the population lives from livestock and agricultural production.
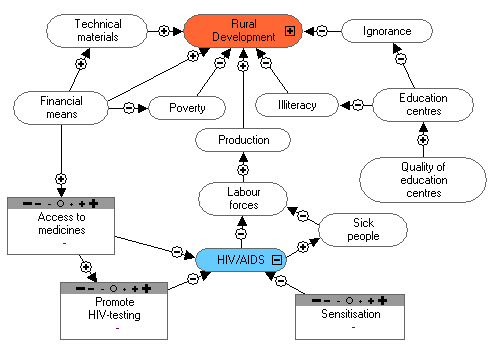
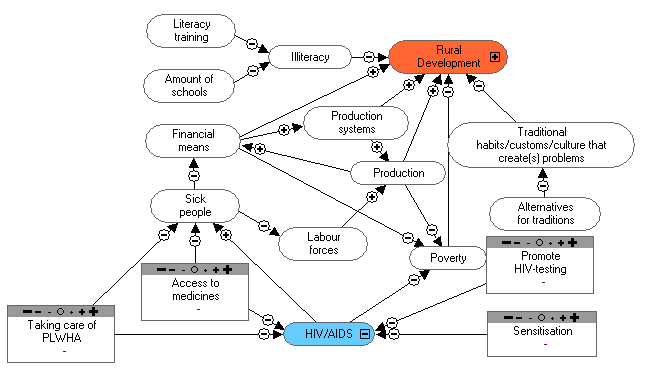
Present HIV/AIDS activities:
- We conduct sensitisatin activities. We let the producers know that AIDS is a scourge.
- After every training or activity (for example: during vacination) we sensitise the people.
HIV/AIDS is an illness, so people need to protect themselves, because they are the key to development.
- We show a video about STI/HIV/AIDS and ask the producers to attend.
- We sensitise collegues and their family members.
|
 |  | Burkina Community Actions Association |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Keita Sidi
Objective: Facilitate in the self-development of
the rural people.
|
 |  | Canadian Centre for Education and International Cooperation |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Adama Ouedraogo
Objectives:
Combat poverty and exclusion:
- Reinforces the development capacities of
disadvantaged communities.
- Supports peace activities, human rights and
equity.
- Mobilise resources and favour information
exchange.
|
 |  | Diebougou Brotherhood Youth Union |
| |
Diebougou, Mr. Luc Somé
Objectives:
1. Stimulate the mind with solidarity, and mutual
understanding between educational and
non-educational youth.
2. Sensitising, making conscious and mobilising
youth groups without questioning their cultural
and socio-economic background.
3. Promoting cultural and sport activities.
4. The creation of activities can improve the
living conditions of the members.
5. Cultural integration through communication
with youth from outside, without discrimination
of race, language, and religion.
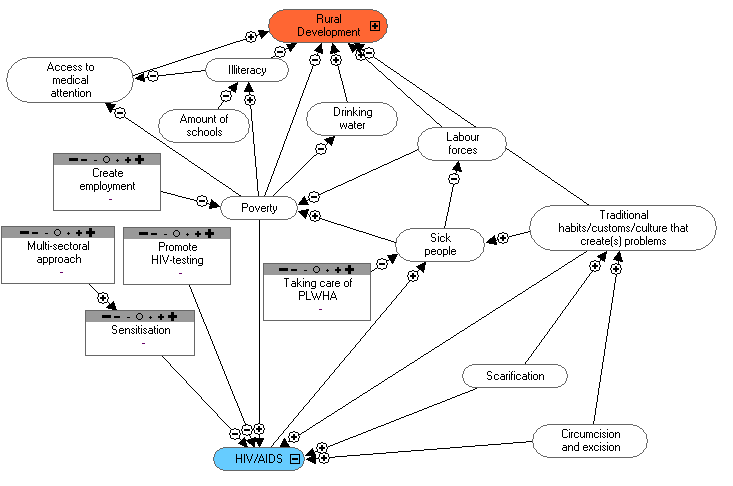
Present HIV/AIDS activities:
Our instructors educate the youth about
STI/AIDS.
STI/AIDS Training:
- Transmission routes
- Family planning
- Unwanted pregnancy
- Conflicts between youth and their parents
- Economic activities
- HIV/AIDS video projection.
- Theatre groups
|
 |  | Diebougou Health District |
| |
Diebougou, Mr. Kini Siaka
Objectives:
The principal objective within the health
structure is to improve the Governmental Health
for the population of Bougouriba province:
- Curative care; relieve sick people
- Promotional care; sensitisation
- Prevention care; vaccination and planning
|
 |  | International Alliance Mission |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Bazemo
Christian organisation.
Objectives:
1. Men being reconciled with God.
2. Integrated human development.
|
 |  | National Federation for Development and Solidarity |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Jean Zoundi
Objectives:
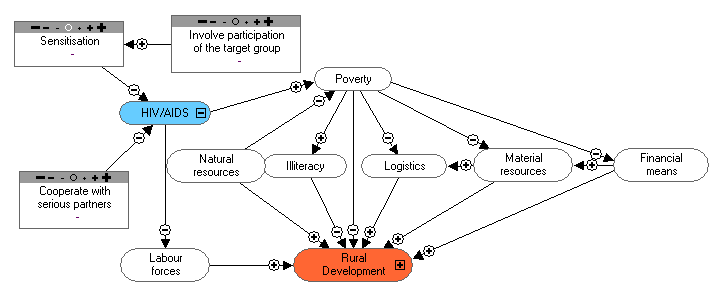
Poverty Alleviation:
- Food security
- Reinforce the organisational capacities of
community based committees, for the
organisational system, training and the income
increases.
|
 |  | Plan Burkina Faso (Plan International) |
| |
Ouagadougou, Dr. Bernabe Yameogo
Plan Burkina Faso is a non-governmental
organisation.
Our objectives cover several domains:
1. Education: 70% children educated in 2011.
2. Drinking water: being able to cover 100% of
the districts with drinking water.
3. Food security: assure food security.
4. Sponsorship: maintain relations with the
sponsors.
5. Health: improve the health status of women
and children.
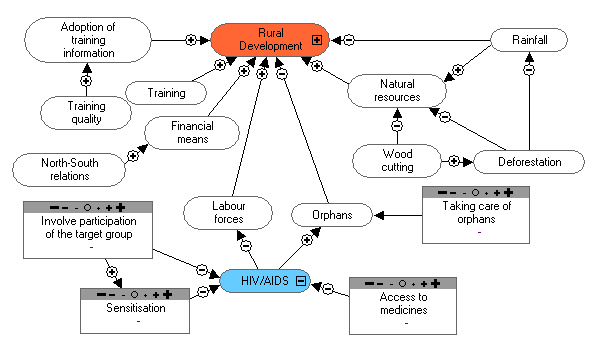
- AIDS: improve the level of knowledge about
HIV/AIDS among the population in order to
reduce the HIV/AIDS prevalence.
|
 |  | Provincial Authories for Education and Literacy Training |
 |  | Provincial Authorities for Agriculture, Water Management and Water Resources |
| |
Diebougou, Mrs. Atala Marie Poda
Objectives:
We carry out the politics within the
governmental structures: promotion of
agriculture, al about water management and
promotion of water resources.
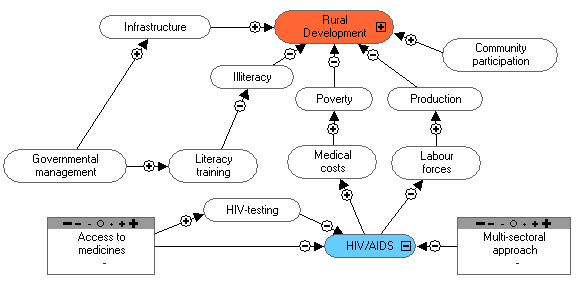
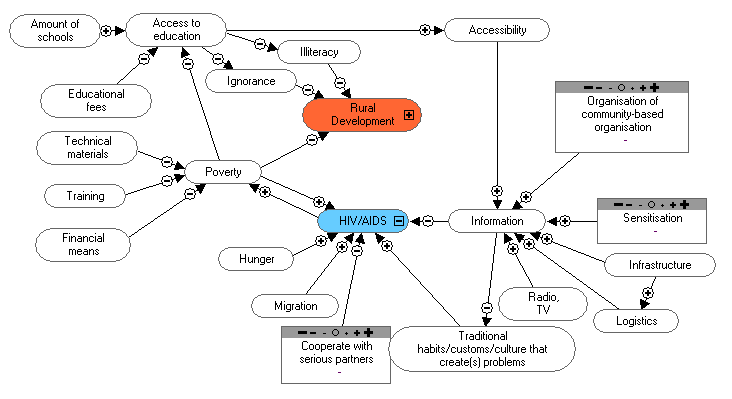
Present HIV/AIDS activities:
There are sub-sections (training for personnel,
families and sensitisation of these groups). At
provincial level there are 2-3 persons in charge
of executing the policies of the fight against
AIDS at organisational level.
After a training program, for example about
agriculture, we spend 15 minutes on AIDS
sensitisation.
|
 |  | Provincial Authorities for Social Service and National Solidarity |
| |
Diebougou, Mr. Daman Siaka
Objectives:
Ministry of Social Work: responsible for social
development:
- Solidarity aspects: political and economic
change
- Social work aspects: children promotion and
protection
- Protection aspects: - family promotion and
protection, - VIH/AIDS sensitisation
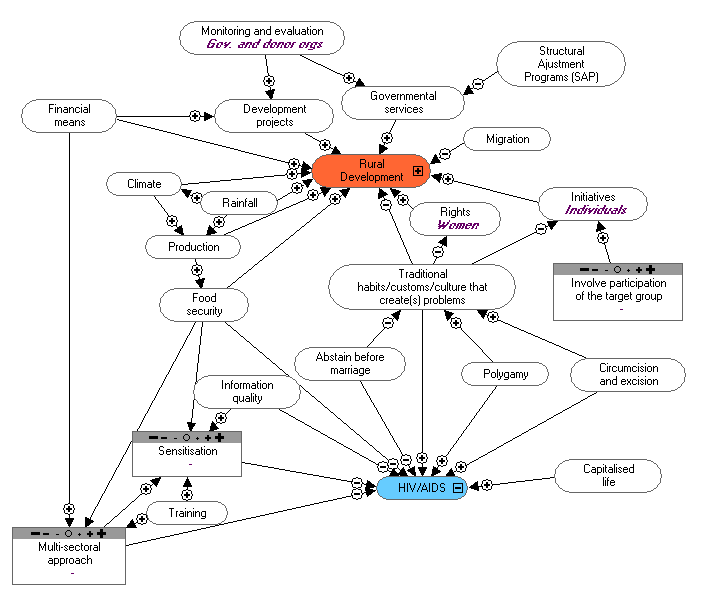
Present HIV/AIDS activities:
Sensitisation and counselling activities:
- Group discussions with children, pupils,
women, men or villagers, and associations.
- Cinema discussions: cassettes with
sensitisation in the local language and in
French. Burkina is working since 1986. The
Health department conduct sensitisation and
care of HIV/AIDS.
|
 |  | Red Cross Burkina Faso |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Louis Zoungrama
Objectives:
1. Alleviate human suffering.
2. Health and life protection.
3. Respect human dignity.
|
 |  | SOS AIDS/Mobilising Youth |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Poda Jean-Marie
SOS AIDS/Mobilising Youth is a non-profitable
community organisation.
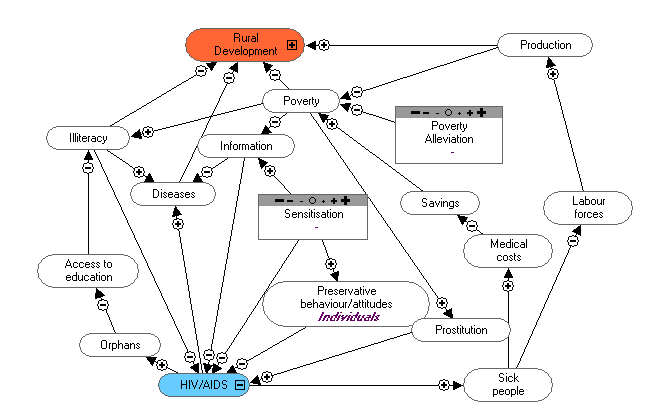
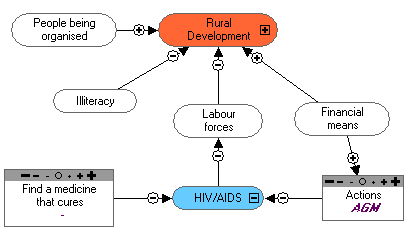
Objectives:
1. Sensitise the population.
2. To promote HIV-testing.
3. To take care of PLWHA.
|
 |  | United Nations Association - International Services |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Sidibe Moussa
Objectives:
1. On the demand of partner organisation we
provide technical assistance.
2. Contribute to the reinforcement of the civil
society.
3. Reinforce the capacities of partner
organisation to prevent being vulnerable within
the society.
4. Support communities and civil society
organisations to get acquainted with and fight
for their rights.
|
 |  | Wend Ve Manegda Rising Gerenation Association |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mr. Michel Koutaba
Objectives:
1. To settle down youth within their village
territory (even as the migrates)
2. Create employment for the settled youth
within their village territory
3. Create income-generating activities for the
youth (20-40 years)
All this to contribute to the research
perspectives of food security. Reduction of
desertification and poverty.
|
 |  | Women-Promotion/Solidarity Development |
| |
Ouagadougou, Mrs. Sawadogo Issiatou
Objectives:
1. To promote and develop women and young
girls.
2. Improve the living-conditions and well being
of women.
3. Fight against the violence towards women.
|